Bio-Chromium 50 µg
- Organically bound chromium from chromium yeast ( ChromoPrecise® )
- Absorbed up to 10 times better than other chromium sources
- Helps maintain normal blood sugar levels in the body
- Contributes to normal macronutrient metabolism
- Manufactured under Danish pharmaceutical control
- Scientifically documented
| 1 tablet contains | % RDA * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium | 50 µg | 125% |
* RDA= Recommended Daily Allowance.
Product Facts
Directions
1 tablet daily, unless advised otherwise. Do not chew the tablet but swallow it whole, preferably during/after a meal.
Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet.
A healthy lifestyle and a varied diet are important for maintaining good health.
Suitable for vegetarians.
Ingredients
Chromium enriched yeast (ChromoPrecise®),
maltodextrin,
bulking agent: microcrystalline cellulose,
anti-caking agents: talc, silica,
glazing agent: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose,
firming agent: magnesium salts of fatty acids.
Storage
Dark, dry and at room temperature.
Keep out of reach of young children.
What is Bio-Chromium 50 µg?
Each tablet of Bio-Chromium contains 50 micrograms of elementary chromium. The chromium used in Bio-Chromium is organic and bound to the yeast's natural amino acids (chromium yeast). It has excellent bioavailability in the body and is absorbed up to 10 times better than other approved chromium sources. Bio-Chromium contains ChromoPrecise®, a unique and patented chromium yeast developed specifically to provide optimal bio-availability. Bio-Chromium has documentation showing that it is manufactured in compliance with the GMP rules (Good Manufacturing Practice) and meets the highest pharmaceutical standards with regard to quality and safety. The effect of the product is documented in a number of published human studies.
Bio-Chromium and yeast
ChromoPrecise does not contain live yeast cells but a chromium-containing, protein-rich powder made from yeast cells. It is only people with yeast allergy who are recommended not to use the product.
From GTF to chromodulin
For many years, it was believed that chromium was included as part of a substance called GTF (Glucose Tolerance Factor). GTF was thought to be a molecule or complex consisting of chromium, niacin (a B vitamin), and the amino acids glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid. The theory behind GTF was only partially supported by science, and the existence of a specific GTF molecule in the body has never been proven.
More recent research, however, has revealed the existence of a unique chrome-binding molecule called chromodulin. It is slightly different than GTF but with the same characteristics and the same health benefits.
The body stores around 4-6 mg of chromium in total. With increasing age, the concentration of chromium in various tissues may drop significantly. This can affect the blood sugar levels and cause cravings for sweets and sugary foods. Snacking may offer temporary relief because of the quick "sugar fix" that delivers intstant energy, but the effect wears off soon after. These cravings can result in weight gain. With a product like Chromium Pharma Nord, you can help your body maintain normal blood sugar levels and prevent these situations from occurring.
What is chromium?
Chromium is an essential trace element that contributes to normal metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (macronutrient metabolism). In addition, chromium supports biological processes involved in maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Chromium acts by entering into a complex of amino acids on the inner surface of the cells, which helps to ensure a steady supply of glucose from the blood.
Chromium can be many things
The effect of a chromium supplement is determined by how effectively the nutrient is absorbed in the body. Normally, we associate chromium with the chromium-plated fixtures in bathrooms or tail pipes on motorbikes. The type of chromium used for industrial purposes is not the same as the chromium needed in human biochemistry. Humans need chromium in its so-called trivalent form. Trivalent means that it is able to form three chemical bonds with other atoms. Industrial chromium is hexavalent, which means it can bond with six other atoms. Inorganically bound chromium usually has a poor bioavailability even though it is trivalent and the form needed by the body.
Lactic acid binds chromium
Trivalent chromium also binds to lactic acid (lactate). Therefore, the body loses a certain amount of chromium when producing large amounts of lactic acid, for example in connection with high-intensity sport, strenuous work, or in situations when the cellular energy production is insufficient.
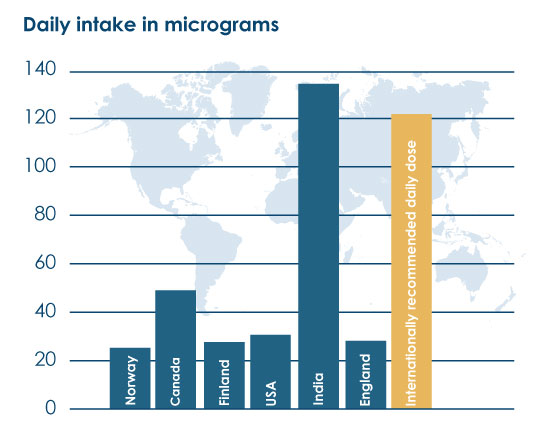
Scandinavian, British, and American dietary analyses show that the average chromium intake is somewhere around 30-40 µg daily. EFSA (the European Food Safety Authority) recommends a daily chromium intake of 40 µg, while WHO has set a safe upper intake level for chromium of 250 µg per day.
What foods contain chromium?
Good natural chromium sources include foods like:
- Shellfish
- Nuts
- Raisins
- Meat
- Beans
- Black pepper
What is blood sugar?
 Blood sugar is a common term for blood levels of glucose, which is the body's energy source. The glucose content goes up after you eat a meal and decreases once the glucose is absorbed by the cells. Blood glucose levels are usually lowest in the morning and highest shortly after you eat.
Blood sugar is a common term for blood levels of glucose, which is the body's energy source. The glucose content goes up after you eat a meal and decreases once the glucose is absorbed by the cells. Blood glucose levels are usually lowest in the morning and highest shortly after you eat.
The hormone insulin plays a crucial role in conveying glucose from the bloodstream into the cells. Chromium assists in the process by enhancing insulin's function. Insulin works from the outside of the eclls, whereas chromium is active on the inside and serves a key that unlocks the cells.
Normal blood sugar values
If you have not eaten for the last six hours, your blood glucose should be lie in the range between 4-7 mmol / L.
Approximately 1.5 hours after eating a meal, yor blood glucose should be <10 mmol / L.
Official claims
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the evidence behind chromium and has acknowledged the following claims:
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels
- Contributes to normal macronutrient metabolism