Pure vitamin D in cold-pressed olive oil for children
- Small pearls with 5 µg (200 IU) of vitamin D3
- Suitable for children over 2 years of age
- Ensures good bioavailability as vitamin D is lipid-soluble
- Vitamin D plays a role in the body's calcium absorption
- Needed for normal growth and devopment of bones in children
- Manufactured under Danish pharmaceutical control
| 1 capsule contains | % RDA* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) | 5 µg | 100% |
*RDA= Recommended Daily Allowance
Products Facts
Dosage
1 capsule daily or as recommended by a physician. To be taken with food and a glass of water. Do not exceed recommended amount. Not suitable for children under the age of 2.
Dietary supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied diet or a healthy lifestyle.
Pregnant and lactating women and those on medication should seek professional advice prior to taking supplements.
Ingredients
Bulking agent: Olive oil
Capsule shell: Gelatin
Humectant: Glycerol, purified water
Colour: Calcium carbonate, Riboflavin
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
Storage
Room temperature and keep out of direct sunlight.
Keep out of reach of children.
What is D-Pearls 5 µg?
 D-Pearls 5 µg is a junior edition of our adult-sized D-Pearls. Each of the tiny soft gelatin capsules contain 5 micrograms (200 IU) of vitamin D3. Their size makes them easy to swallow. The vitamin D is dissolved in cold-pressed olive oil to improve absorption in the digestive system, as vitamin D is a lipid-soluble vitamin. Research shows that this product is easily absorbed in the body. D-Pearls 5 µg is suitable for children over 2 years of age.
D-Pearls 5 µg is a junior edition of our adult-sized D-Pearls. Each of the tiny soft gelatin capsules contain 5 micrograms (200 IU) of vitamin D3. Their size makes them easy to swallow. The vitamin D is dissolved in cold-pressed olive oil to improve absorption in the digestive system, as vitamin D is a lipid-soluble vitamin. Research shows that this product is easily absorbed in the body. D-Pearls 5 µg is suitable for children over 2 years of age.
D-Pearls and children
Vitamin D is extremely important during childhood because the nutrient plays an important role in supporting normal growth and bone development. It is important for children to get exposed to a sufficient amount of sunlight whenever the weather conditions are right to help them synthesize vitamin D in their skin. However, with a supplement like D-Pearls Junior, it is easy to ensure an adequate vitamin D status throughout the year.
Vitamin D supplements (as drops) are recommended for children in the age group 0-2 years. From that point on, a vitamin D in capsule form is the best choice. The small gelatin capsules are easy for children to chew or swallow. You can even pierce the capsule and squeeze its content into food or liquid.
Safety and quality
Pharma Nord's factory in Vojens, Denmark, manufactures both pharmaceutical drugs and dietary supplements. The company has chosen to manufacture all its products in compliance with pharmaceutical guidelines and rules for quality inspection. That way, consumers will always know that any Pharma Nord product meets the highest standards for quality, effect, and safety.
Minor variations may occur in the firmness of the vitamin D capsules due to fluctuations in temperature and humidity. Product tests carried out in our climate chambers show that this does not in any way affect the quality or the effect of the preparation.
D-Pearls has been on the European market since 2007.
What is vitamin D?
 Like most other vitamins, vitamin D is essential. There are several kinds of vitamin D but the two most important forms are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is the form of the vitamin that we synthesize in our skin when we are exposed to sufficient amounts of sunlight. Sunlight is our main source of vitamin D but the synthesis is only possible when the sun sits sufficiently high in the sky. In large parts of Europe, this is limited to the period from April through September.
Like most other vitamins, vitamin D is essential. There are several kinds of vitamin D but the two most important forms are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is the form of the vitamin that we synthesize in our skin when we are exposed to sufficient amounts of sunlight. Sunlight is our main source of vitamin D but the synthesis is only possible when the sun sits sufficiently high in the sky. In large parts of Europe, this is limited to the period from April through September.
Vitamin D2 is only available from the diet. It is produced by certain fungi and plants when they are exposed to ultraviolet light. Both vitamin D2 and D3 require subsequent activation in the liver and kidneys in order to become biologically active. Science used to believe that both forms of vitamin D were equally effective in the body. However, depending on what method is used to measure their effectiveness, vitamin D3 is 56-87 per cent more effective than vitamin D2 in terms of raising blood levels of vitamin D. Moreover, D3 is stored in fat tissue more than three times as effectively as D2.
* Heaney RP, et al. Vitamin D3 Is More Potent Than Vitamin D2 in Humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010.
Children require relatively more vitamin D than adults.
Vitamin D has an array of important functions in the body. For instance, vitamin D:
- is important for normal cell division
- helps maintain normal bones and teeth
- contributes to normal absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphorus
- plays an important role in the body's immune system and muscle function
Good vitamin D sources
It is difficult to get a sufficient amount of vitamin D from the diet alone, partly because one of best sources of the nutrient is oily fish such as salmon, herring, and mackerel, and people generally do not eat all that much fish. Vitamin D is also found in limited amounts in meat, milk, and eggs. In the plant kingdom, vitamin D is available in small amounts in certain fungi. The best dietary sources of vitamin D are:
|
|
Cooking, baking, and frying result in a certain loss of vitamin D from foods.
The need for vitamin D
 Vitamin-D supplements are generally recommended for:
Vitamin-D supplements are generally recommended for:
- Children aged 0 – 2 years (vitamin D as drops)
- Pregnant women
- Children and adults with dark skin
- Children and adults who wear fully covering clothes in the summer time
- People who do not spend time outdoors in the daytime or generally avoid sunlight
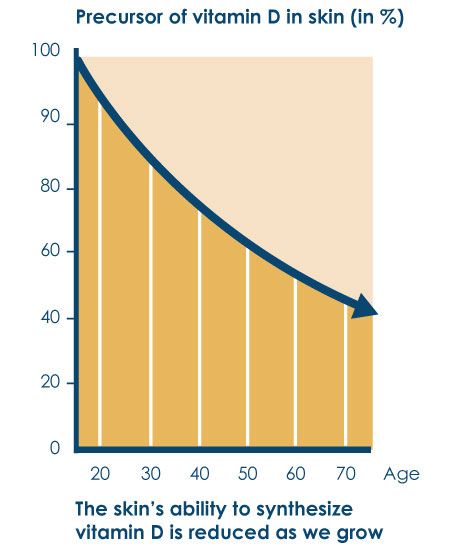
- Nursing home residents. Older people have reduced vitamin D synthesis in their skin, and their intestinal absorption of vitamin D is also reduced
- People older than 70 years of age
- Anyone at increased risk of osteoporosis, regardless of their age
Vegans and vegetarians are advised to adhere to the official guidelines for sun exposure and possibly take a supplement of vitamin D during the winter period.
Blood levels of vitamin D can be determined by a blood test that measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-(OH)D) and is expressed in nmol/L. Vitamin D status is graduated in the following way:
- <12 nmol/L: Severe deficiency
- 12-25 nmol/L: Deficiency
- 25-50 nmol/L: Insufficiency
- >50 nmol/L: Sufficiency
- 75-150 nmol/L: Optimal level in individuals with fragile bones and kidney patients
- >ca. 200 nmol/L: Risk of overdose
> = greater than
< = less than
Vitamin D conversion
- 1 nmol/L = 0,4 ng/ml
- 5 µg = 200 IU (international units)
Measurement of vitamin D
The best way to determine your vitamin D status is a blood test. Normal, healthy individuals who eat a balanced diet and are exposed to sunlight generally don't have to worry about their vitamin D status, but certain groups are advised to have their vitamin D levels checked. Science has found that people with dark skin synthesize less vitamin D in their skin that light-skinned people. There is also a relation between low vitamin D status in the blood and overweight and obesity, which is because vitamin D is stored in the body's fat tissue.
Besides obvious vitamin D-limiting factors such as lack of sunlight and unhealthy eating habits, there are more subtle things that can have a negative impact on your vitamin D status. For example, certain types of medicine may impair the body's absorption of vitamin D, thereby increasing the need for the nutrient.
Variations in gelatin hardness
The hardness of our soft gelatin capsules can vary. The difference depends solely on the water content of the capsule shell. We dry all our soft capsules before packaging, which makes the capsules firmer and facilitates the packaging process itself. Over time, the capsules can absorb water from the air, and this will soften the capsule shell.
The variations in the hardness of the capsule have no effect on the product quality, but if a hard capsule is a problem, a solution may be to leave the capsule outside the blister sheet for a day, whereby the capsule can absorb a little water from the air. This is generally not something we recommend, as the product will no longer be protected as when it is in the blister sheet. Another method of quickly softening the gelatin capsule is to place it in lukewarm water for one minute. However, it should be seen as an emergency solution.
Official claims
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the evidence behind vitamin D and has acknowledged the following claims:
- Contributes to normal absorption/utilization of calcium and phosphorus
- Contributes to normal blood calcium levels
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal muscle function
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal teeth
- Contributes to normal function of the immune system
- Has a role in the cell division process

